Summary:When it comes to energy bills, one of the key components is your energy meter. It shows how much ele...
When it comes to energy bills, one of the key components is your energy meter. It shows how much electricity and gas you're using each month and allows you to top up by text, app or online at any time of the day or night.
In many cases, if you don't pay your bill on time or can't afford to, your supplier may try to move you onto a prepayment meter as part of a debt solution. However, it's important to note that not all households are affected by this.
You can ask to be moved off a prepayment meter if it's no longer practical for you or if your circumstances have changed in any way. These include things like a change in your employment status or a move to a new property that's not within a suitable distance from a meter point, where you can top up.
There are also rules in place for disabled or ill people who may struggle to get to or read their meter. In some cases, suppliers are allowed to install a shunt, which bypasses your meter and lets you read your meter from your bed, for example.
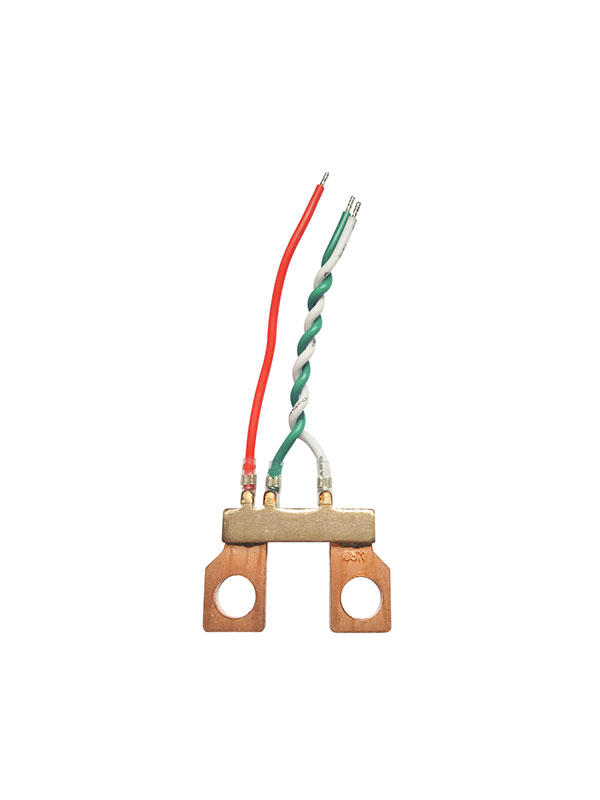
Shunts have a low resistance, which means that they are able to measure the flow of current in the meter without having to connect your meter directly to your power supply. This can help you to cut down on your energy usage and save money by reducing your overall bill.
The shunt used in your prepayment meter will depend on its specifications, but you should always ask for a shunt that matches the type of meter you have and can handle the current you need to measure.
Typically, a shunt is made from a high-conductivity material such as copper or aluminum to minimize the resistance and ensure accurate current measurements. They are also available in a range of shapes and sizes, depending on the application.
They can also be programmed to provide different current measurements. This is a feature that can be useful for industrial and commercial applications, where accuracy and precision are essential.
A shunt can also be used to measure the voltage drop across your meter, which is another way of measuring the amount of current you are using. The voltage drop across the shunt is proportional to the amount of current passing through it.
There are several types of shunt that can be used with a meter to measure the current, including a precision shunt, a programmable shunt and a standard shunt.
Precision shunt: This is a shunt that is designed for precision and stability, with high-precision current measurement capabilities. This type of shunt is usually used for scientific experiments or research, and it can be programmed to provide the exact current you need to use.
Programmable shunt: This is a programmable shunt that can be programmed to provide the exact current measurements you need, which can be useful for industrial and commercial applications.